Research
This includes past or ongoing research projects as well as other interests I intend to pursue in the near future. These works can be broadly classified into application- and development-oriented projects.
This section will be updated periodically.
An Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis of Astrocyte–Immune Interactions in Glioblastoma
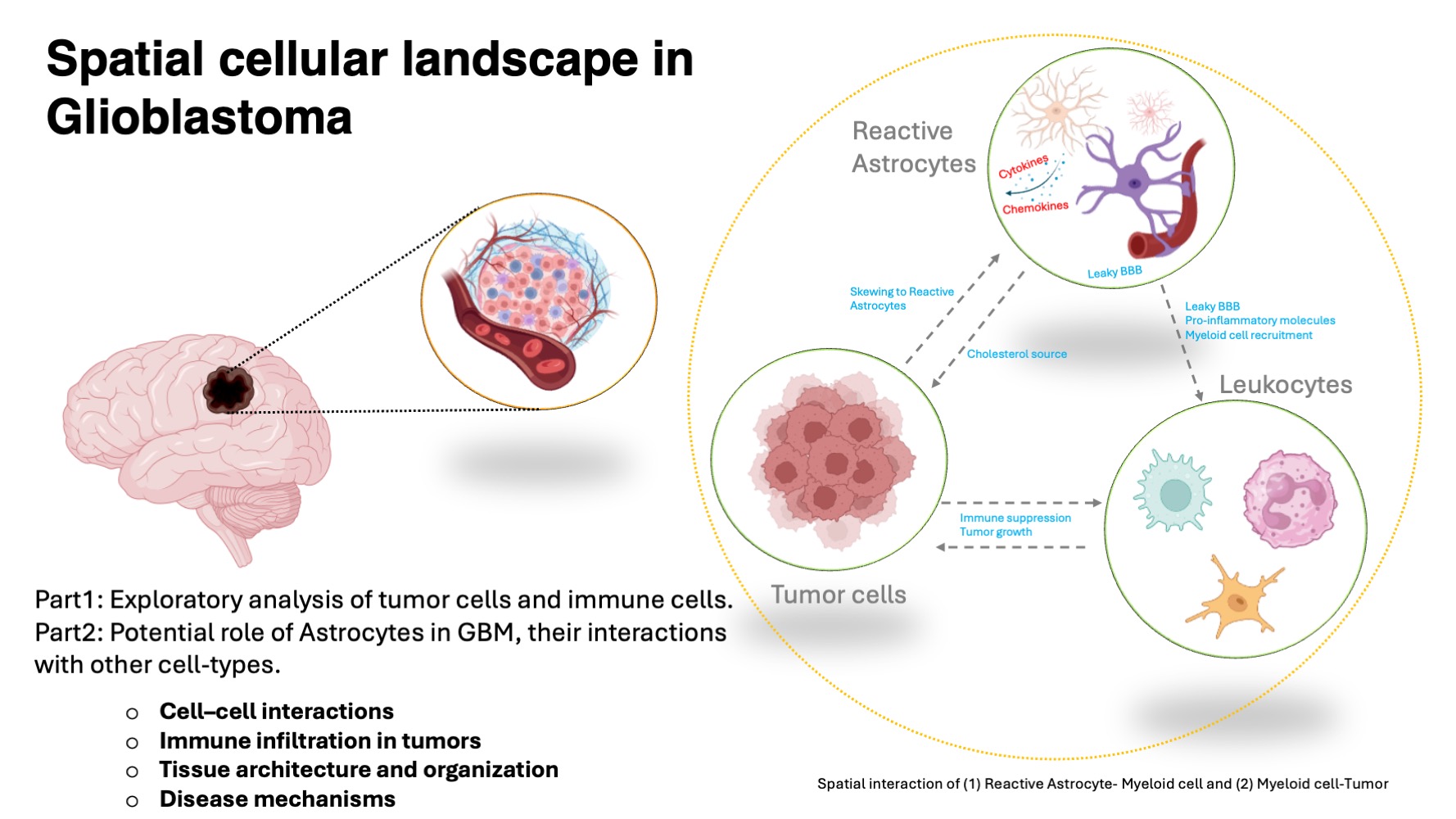
This study investigates astrocyte–immune cell interactions using an integrated multi-omics approach, combining transcriptomic, spatial transcriptomic/proteomic, and spatial analyses to define cellular crosstalk within the glioblastoma tumor microenvironment.
Characterizing MAIT Cells in Glioblastoma
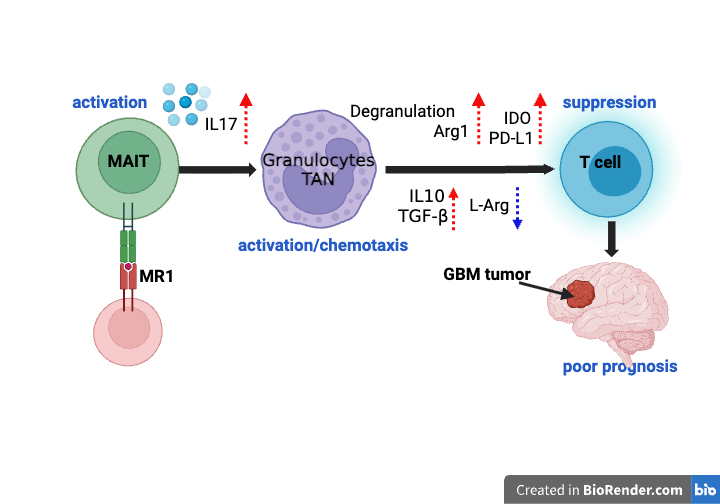
We used TCR sequencing, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and multiplex tissue imaging (CODEX) to investigate the role of mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells in glioblastoma (GBM). MAIT cells were present within GBM tumors and associated with immunosuppressive myeloid cells. Increased MAIT cell abundance correlated with poor patient survival in the TCGA-GBM cohort. Functional analyses suggest an immunosuppressive role mediated through IL-17 signaling.
Highlights
- MAIT cell gene signatures correlate with poor survival in GBM
- MAIT17 cells are the dominant MAIT subset in GBM tumors
- MAIT cells contribute to immunosuppression via tumor-associated neutrophils
Publication:
Keretsu, S., Hana, T., Lee, A., Kedei, N., Malik, N., Kim, H., … Terabe, M. (2025).
Characterization of MAIT cells in glioblastoma reveals a potential immunosuppressive role through a
MAIT–Neutrophil axis. Neuro-Oncology Advances, 7(1), vdaf173.
More details regarding my multi-omics projects will be updated soon.
Virtual Screening of MEROPS for SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors
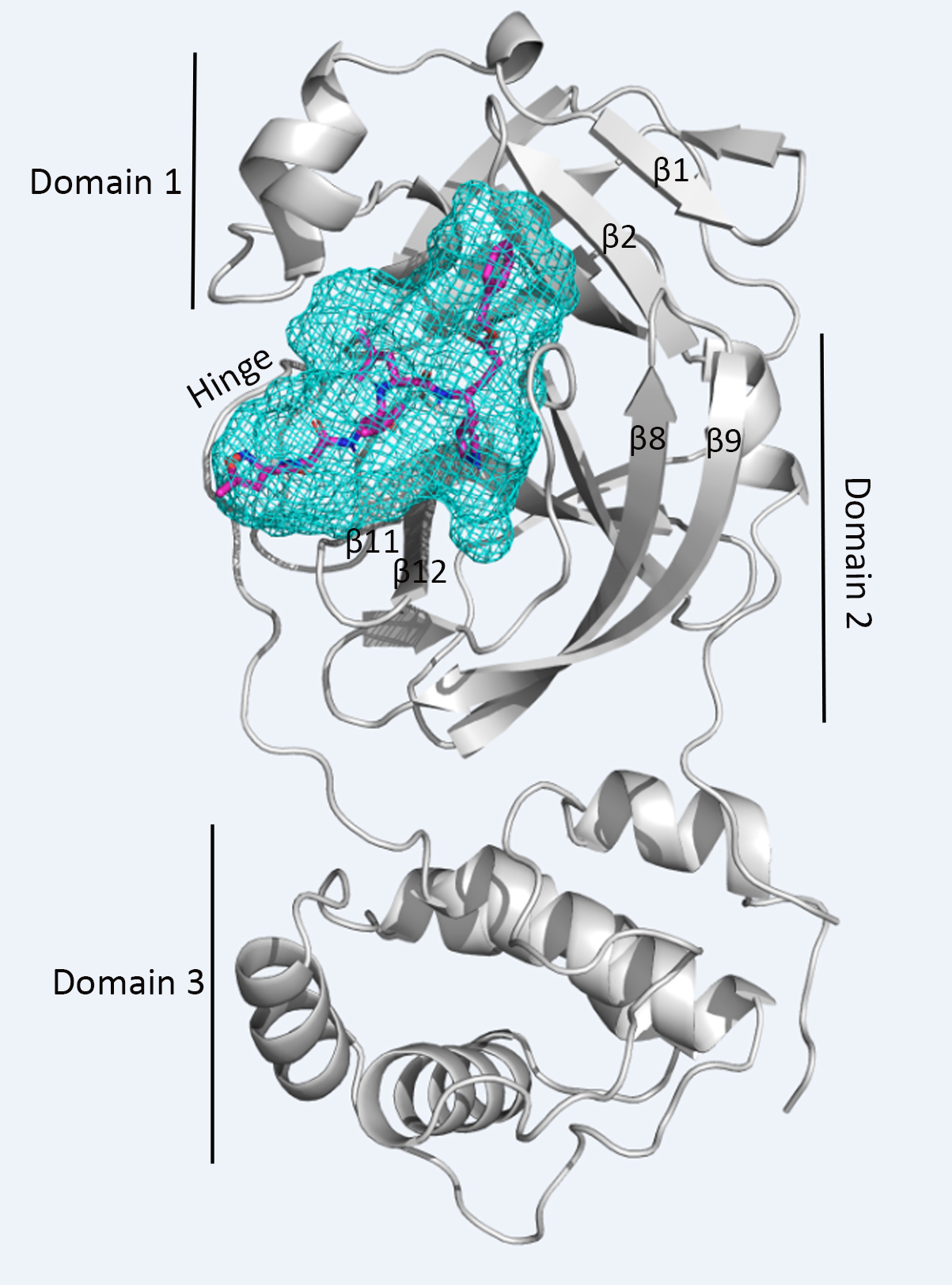
Using the crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro (PDB: 6LU7), we identified potential inhibitors from the MEROPS protease agonist and antagonist database. Several candidates showed higher predicted binding affinity than the co-crystallized inhibitor.
Publication:
Keretsu, S., Bhujbal, S. P., & Cho, S. J. (2020).
Rational approach toward COVID-19 main protease inhibitors via molecular docking, molecular dynamics
simulation and free energy calculation. Scientific Reports, 10, 17716.
Identification of Protein Complexes in Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks
Proteins rarely act alone in the cell. Instead, they work together in groups called protein complexes to carry out essential biological functions. Understanding how these complexes form and function is important for advancing basic biology and improving our knowledge of disease mechanisms. Scientists often use protein–protein interaction networks to identify protein complexes, but many existing methods assume these networks are static and focus mainly on finding tightly connected groups of proteins. As a result, some important complexes may be missed. In this study, we present a new computational approach called Weighted Edge-based Clustering (WEC) to improve the detection of protein complexes. Rather than relying only on how many connections proteins have, WEC evaluates the strength of interactions between proteins by combining information about network structure with patterns of gene expression. This allows the method to identify groups of proteins that are both strongly connected and biologically coordinated. When tested on multiple real-world biological datasets, WEC identified protein complexes more effectively than several widely used existing methods. By better reflecting the dynamic and functional nature of protein interactions, this approach provides a valuable tool for studying cellular organization and may support future research into the molecular basis of health and disease.
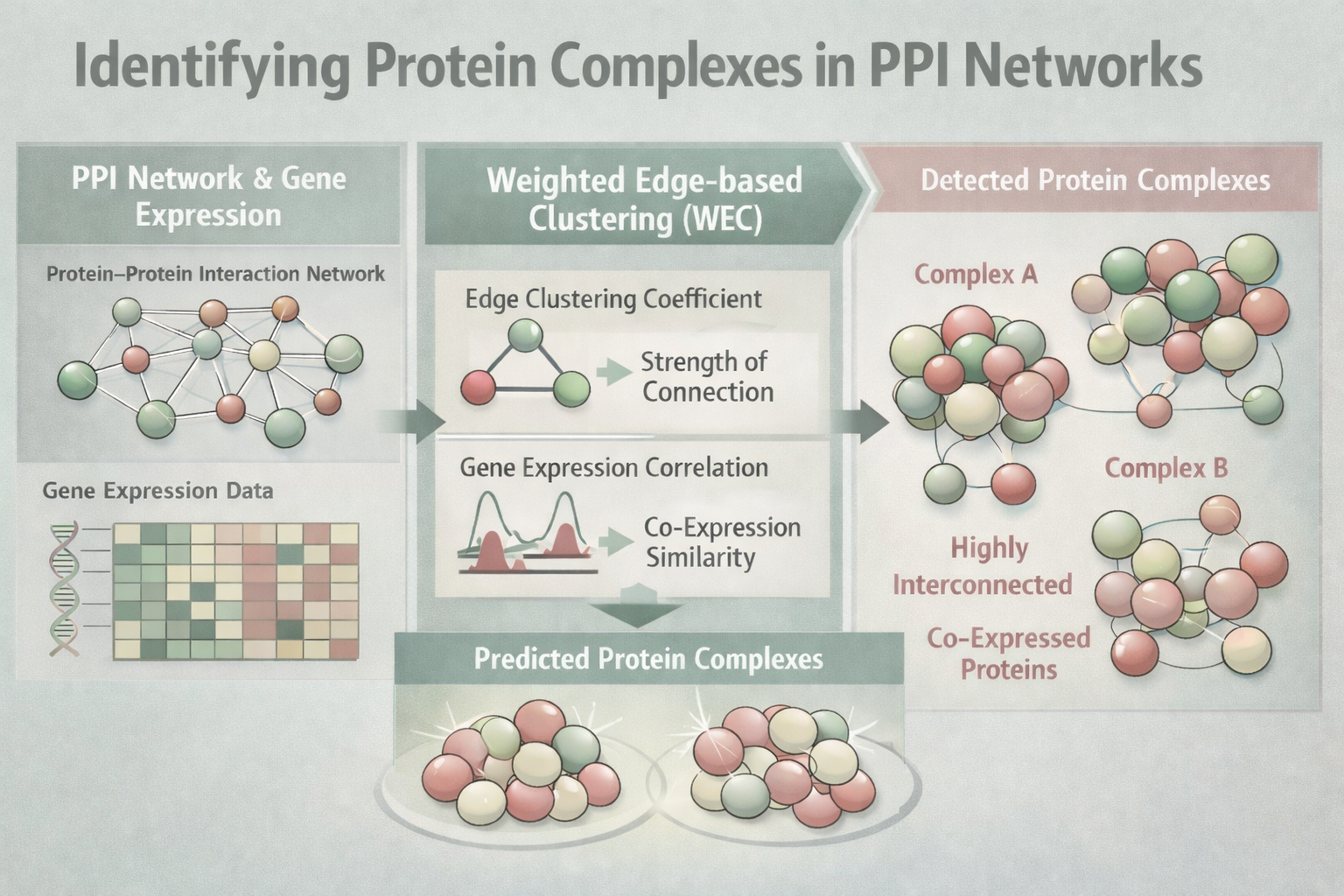
Algorithm 1
Publication:
Keretsu, S., & Sarmah, R. (2016).
Weighted edge based clustering to identify protein complexes in protein–protein interaction networks
incorporating gene expression profile. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 65, 69–79
Computational Study of Serotonin Receptors (GPCR)
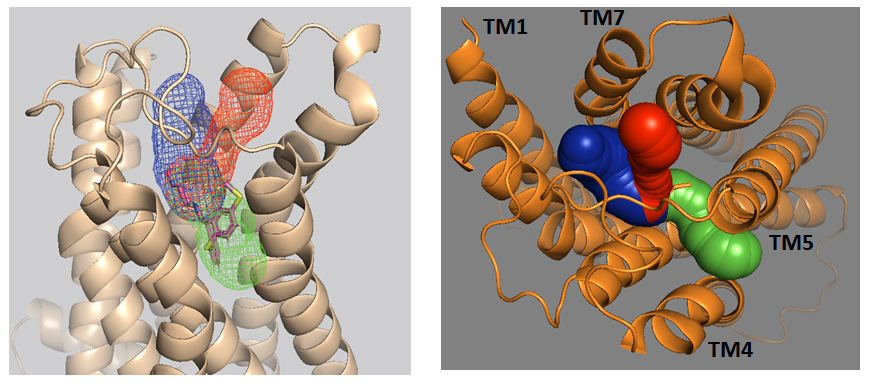
Recent studies demonstrate that Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD) can effectively probe binding and activation mechanisms of GPCRs. This work explores whether enhanced sampling methods can resolve unresolved structural questions in serotonin receptors.
Mechanism of STING Agonism
STING activation is critical for innate immune signaling and cancer immunotherapy. This project focuses on mechanistic understanding and rational design of hydrolysis-resistant STING agonists using computational drug discovery approaches. …More